Blocks in Blockchain refer to the data structures where transaction data is permanently stored. Each block contains a verified and validated set of transactions and is closed when all the transactions have been validated by the network. Thus, a new block is created which holds the next set of transactions, and that’s how the blocks are formed into a chain of blocks, giving the disruptive technology its popular name.
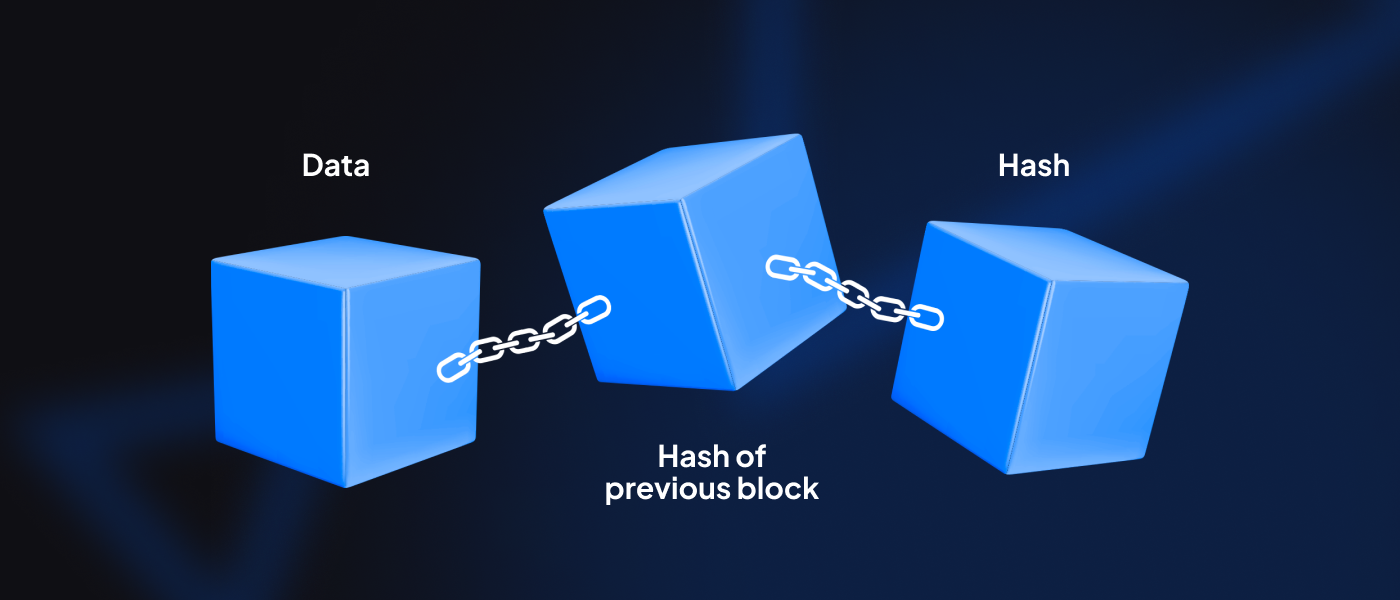
Each block contains a unique identifier referred to as a “hash,” a hash of the previous block, and timestamped batches of recent transactions that have been validated. The role of the previous hash on each block is to keep it linked to the rest of the blocks in the chain and prevent them from being altered or a new block being inserted between two blocks. Each hash-encrypted block is what makes blockchain impenetrable and tamper-proof.
Apart from the hash, each block contains the following information:
Magic number – The number comprising a set of values that identifies the block as a part of that particular blockchain network.
Blocksize – This sets down the specific size of the block so that it can limit the number of transactions that can be stored on it.
Block header – Contains further information about the block.
Transaction counter – A number that reflects the number of transactions stored on the block.
Transactions – The list of transactions stored on the particular block.
The transaction element further includes the following:
Timestamp – This also helps place the block in the blockchain and give it its unique identity.
Hash Merkel root – hash of the transactions in the binary hash trees (also known as the Merkel tree) of the current block.
Version – The cryptocurrency version being used.
Previous block hash – Contains the encrypted number mentioned in the header of the preceding block to ensure no new block can be inserted in between.
Nonce – The encrypted puzzle (number) that the miner needs to solve that lets them verify the block and close it.
Bits – This signifies the difficulty level of the nonce.
Now that we know what blocks are, let us dive a bit deeper and understand what blockchain is and what it comprises.
What is a blockchain?
A blockchain is a distributed database that comprises a list of ordered records, called blocks, that grow continuously. The chain that links these blocks with each other is cryptography. As mentioned previously, each block contains multiple transaction data, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash for that block and the one preceding it.
What are the benefits of blockchain?
Many people strive to understand why did the world need blockchain when everything was running smoothly with current tech. While the primary benefit of blockchain is to act as a database for recording transactions, there are three more benefits that have made it the popular technology it is today.
Cost savings – Blockchain removes the double effort needed to process and record transactions as participants have access to a shared ledger. This means transactions need lesser oversight resulting in cost savings.
Time savings – Since there is no central authority involved, blockchain reduces transaction time to mere minutes.
Better security – Probably the best feature to follow its role as a database is the security it offers against fraud, cybercrime, and tampering, given its encrypted hash system.
What are the Key Concepts behind blockchain?
For any blockchain to work, there are 4 things that are needed.
An “append-only” distributed system of records, the shared ledger is shared across a business network. This is what makes blockchain unique as it offers a single ledger as compared to the double ledgers maintained in traditional businesses.
Permissions are key to ensuring that all transactions are authenticated, verifiable, and secure. Blockchain can constrain network participation which helps organizations adhere to data protection regulations like HIPAA and GDPR more easily.
Smart contracts are essentially “an agreement or set of rules that govern a business transaction.” They are stored on the blockchain and automatically executed as soon as the set of rules is met and the business transaction goes through.
This is the mechanism that powers the decentralized nature of blockchain. The consensus mechanism ensures that all stakeholders are on the same page when it comes to verifying transactions. Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), and multisignature are some of the types of consensus mechanisms that are practiced in Blockchain right now.
Who are the Key Players in the Blockchain ecosystem?
There are multiple parties involved in any Blockchain. There are the users, the network operators, the regulators, and the authorities.
Let us take a closer look at each of them.
Blockchain users
Users are the people who use the blockchain for their own purposes, such as making payments or transferring data.
Miners
Miners are responsible for verifying transactions and adding them to the blockchain. In the case of Bitcoin, miners solve complex cryptographic puzzles to win the right to mine the next block of transactions for which they get paid in the cryptocurrency, that is $BTC.
Developers
Developers create applications that use the blockchain and build new tools to enhance the blockchain’s functionality.
Investors
Investors provide the capital necessary to maintain and grow the blockchain.
Network operators
Participants who have special permission to create, monitor, and manage the network.
Regulators
Blockchain users with special permission to oversee the transactions happening in the network.
Certificate authorities
Individuals who are responsible for issuing and managing the various types of certificates needed to run a permissioned blockchain network.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blocks are the building blocks of blockchain technology. They are digital records that contain information about transactions and other data, and they are secured by the consensus mechanism used in the blockchain. There are several stakeholders in a blockchain network, including miners, developers, users, and investors. Each of these stakeholders has an important role to play in ensuring the success of the blockchain.